
Biofertilizers are emerging as a catalyst for change in the agriculture industry. These organic alternatives are often overlooked but are proving to be an eco-friendly and sustainable way to nourish crops. By enhancing soil health and boosting crop productivity, biofertilizers are transforming traditional farming practices and offering a promising narrative of harmony between human cultivation and the natural world.
In this exploration of biofertilizers, we will take a closer look at their organic origins and the microbial symphony that unfolds within the soil. We will delve into their profound impact on soil health, including their role in fortifying soil structure, fostering nutrient availability, and even defending against invasive pathogens. Moreover, we will showcase real-world success stories and discuss the diverse types of biofertilizers tailored to meet the unique needs of different crops.
Join us on this journey into the world beneath the surface, where microscopic allies collaborate with nature to rewrite the script of traditional agriculture, promising a greener and more resilient future for our crops and soils. blog isn’t just about fertilizers; it’s an ode to a paradigm shift in agriculture. We’ll provide insights into the application techniques that unlock the full potential of biofertilizers and address common myths, ensuring a clearer understanding of their benefits.
So, fasten your seatbelt as we journey into the heart of sustainable agriculture, where biofertilizers are the unsung heroes, working tirelessly to cultivate a tomorrow that is not just fruitful but also rooted in harmony with nature. Welcome to the revolution – welcome to the world of biofertilizers.
Benefits of Bio-Fertilizers

- Promotion of Plant Growth: These microbial-based fertilizers actively contribute to the stimulation of plant growth, fostering healthier and more vigorous crops.
- Improved Nutrient Uptake: Biofertilizers enhance nutrient availability in the soil, leading to an efficient uptake of essential Enhanced Soil Fertility: Biofertilizers play a crucial role in augmenting the fertility of soil, creating an environment conducive to robust plant growth elements by plants for their optimal development.
- Nitrogen Fixing from Atmosphere: One key benefit is their capacity to fix atmospheric nitrogen, converting it into forms usable by plants, thus reducing the need for nitrogenous fertilizers.
- Reduction in Dependency on Chemical Fertilizers: By utilizing biofertilizers, farmers can minimize their reliance on chemical fertilizers, mitigating potential environmental pollution and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
- Minimized Environmental Impact: The decreased use of chemical fertilizers results in a lowered environmental footprint, contributing to the conservation of ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Support for Sustainable and Eco-friendly: Farming Practices: Biofertilizers align with the principles of sustainable agriculture, fostering environmentally friendly practices that ensure long-term soil health and productivity.
- Overall Contribution to Healthier Crops and Ecosystems: The holistic impact of biofertilizers extends beyond individual crops, positively influencing the overall health and balance of agricultural ecosystems.
Types of Biofertilizers
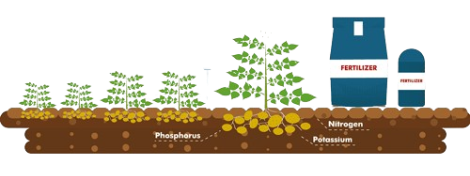
- Nitrogen-Fixing Biofertilizers- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, such as Rhizobium and Azotobacter, form a significant category. They establish symbiotic relationships with certain plants, particularly legumes, enhancing soil nitrogen levels by converting atmospheric nitrogen into a form usable by plants. This promotes better plant growth and reduces the need for nitrogen-based chemical fertilizers.
- Phosphate-Solubilizing Biofertilizers- Phosphorus is crucial for plant development, and phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms like bacteria and fungi aid in making phosphorus more accessible to plants. These biofertilizers enhance phosphate solubility in the soil, improving nutrient absorption and contributing to root development.
- Potassium-Releasing Biofertilizers-Microorganisms like Bacillus and Clostridium are known for their ability to release potassium from mineral sources in the soil. Potassium is vital for plant metabolism and stress tolerance. These biofertilizers help maintain optimal potassium levels, enhancing plant resilience and overall health.
- Symbiotic Mycorrhizal Fungi- Mycorrhizal fungi establish symbiotic relationships with plant roots, forming a network that extends the plant’s root absorption capacity. This enhances nutrient uptake, particularly phosphorus and micronutrients, leading to improved plant growth, root development, and stress resistance.
- Azospirillum Biofertilizers-Azospirillum is a type of nitrogen-fixing bacteria that works with non-leguminous plants. It promotes plant growth by facilitating nutrient absorption, synthesizing growth-promoting substances, and enhancing root development. Azospirillum biofertilizers are particularly beneficial for cereals and grasses.
- Organic Residue Decomposers- Certain biofertilizers focus on breaking down organic residues in the soil. Microorganisms like Trichoderma and Pseudomonas contribute to the decomposition of crop residues, making nutrients more available for subsequent crops. This process supports sustainable agriculture by recycling organic matter
The Essence of Biofertilizers:

Biofertilizers, in essence, are natural fertilizers that contain living microorganisms, mainly bacteria, fungi, and algae, which contribute to the enrichment of soil nutrients. Unlike traditional chemical fertilizers, biofertilizers harness the power of nature’s own processes to enhance plant growth and yield.
- Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria: Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, such as Rhizobium and Azotobacter, form a significant category. They establish symbiotic relationships with certain plants, particularly legumes, enhancing soil nitrogen levels by converting atmospheric nitrogen into a form usable by plants. This promotes better plant growth and reduces the need for nitrogen-based chemical fertilizers.
- Phosphorus-Solubilizing Fungi: Phosphorus, an essential nutrient for plant development, is often present in the soil in an insoluble form. Enter phosphorus-solubilizing fungi – nature’s own problem solvers. These fungi break down the complex compounds, making phosphorus more accessible to plants. This biofertilizer not only improves nutrient availability but also aids in root development and overall plant.
- Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR):PGPR is a group of bacteria that establishes a beneficial relationship with plant roots. These bacteria produce growth-promoting substances, enhance nutrient uptake, and protect plants from pathogens. The symbiosis between PGPR and plants acts as a natural defense mechanism, reducing the reliance on chemical pesticides.
The Environmental Advantage:
The use of biofertilizers aligns with the principles of sustainable agriculture. Unlike chemical fertilizers, which may lead to soil degradation over time, biofertilizers contribute to the long-term improvement of soil structure and fertility. Moreover, they play a crucial role in reducing the environmental impact associated with conventional farming practices.
Farmers’ Perspective:
Farmers worldwide are increasingly recognizing the benefits of incorporating biofertilizers into their agricultural practices. Beyond enhancing soil health and crop productivity, the use of biofertilizers often results in cost savings, as they reduce the need for expensive synthetic fertilizers.
Conclusion:
As we navigate the challenges of feeding a growing global population while safeguarding our environment, biofertilizers emerge as a beacon of hope. Their ability to harness natural processes to enrich soil, promote plant growth, and reduce environmental impact positions them as a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture. Embracing biofertilizers is not just a choice for the present; it’s an investment in a healthier, more resilient future for our planet and its inhabitants.

Leave a Reply